Oxford: Smooth Fit to Log-Odds Ratios¶
An example from OpenBUGS [38] and Breslow and Clayton [9] concerning the association between death from childhood cancer and maternal exposure to X-rays, for subjects partitioned into 120 age and birth-year strata.
Model¶
Deaths are modelled as
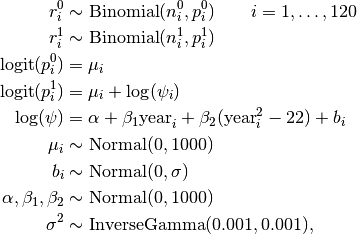
where 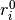 is the number of deaths among unexposed subjects in stratum
is the number of deaths among unexposed subjects in stratum 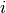 ,
, 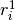 is the number among exposed subjects, and
is the number among exposed subjects, and 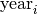 is the stratum-specific birth year (relative to 1954).
is the stratum-specific birth year (relative to 1954).
Analysis Program¶
using Mamba
## Data
oxford = (Symbol=> Any)[
:r1 =>
[3, 5, 2, 7, 7, 2, 5, 3, 5, 11, 6, 6, 11, 4, 4, 2, 8, 8, 6, 5, 15, 4, 9, 9,
4, 12, 8, 8, 6, 8, 12, 4, 7, 16, 12, 9, 4, 7, 8, 11, 5, 12, 8, 17, 9, 3, 2,
7, 6, 5, 11, 14, 13, 8, 6, 4, 8, 4, 8, 7, 15, 15, 9, 9, 5, 6, 3, 9, 12, 14,
16, 17, 8, 8, 9, 5, 9, 11, 6, 14, 21, 16, 6, 9, 8, 9, 8, 4, 11, 11, 6, 9,
4, 4, 9, 9, 10, 14, 6, 3, 4, 6, 10, 4, 3, 3, 10, 4, 10, 5, 4, 3, 13, 1, 7,
5, 7, 6, 3, 7],
:n1 =>
[28, 21, 32, 35, 35, 38, 30, 43, 49, 53, 31, 35, 46, 53, 61, 40, 29, 44, 52,
55, 61, 31, 48, 44, 42, 53, 56, 71, 43, 43, 43, 40, 44, 70, 75, 71, 37, 31,
42, 46, 47, 55, 63, 91, 43, 39, 35, 32, 53, 49, 75, 64, 69, 64, 49, 29, 40,
27, 48, 43, 61, 77, 55, 60, 46, 28, 33, 32, 46, 57, 56, 78, 58, 52, 31, 28,
46, 42, 45, 63, 71, 69, 43, 50, 31, 34, 54, 46, 58, 62, 52, 41, 34, 52, 63,
59, 88, 62, 47, 53, 57, 74, 68, 61, 45, 45, 62, 73, 53, 39, 45, 51, 55, 41,
53, 51, 42, 46, 54, 32],
:r0 =>
[0, 2, 2, 1, 2, 0, 1, 1, 1, 2, 4, 4, 2, 1, 7, 4, 3, 5, 3, 2, 4, 1, 4, 5, 2,
7, 5, 8, 2, 3, 5, 4, 1, 6, 5, 11, 5, 2, 5, 8, 5, 6, 6, 10, 7, 5, 5, 2, 8,
1, 13, 9, 11, 9, 4, 4, 8, 6, 8, 6, 8, 14, 6, 5, 5, 2, 4, 2, 9, 5, 6, 7, 5,
10, 3, 2, 1, 7, 9, 13, 9, 11, 4, 8, 2, 3, 7, 4, 7, 5, 6, 6, 5, 6, 9, 7, 7,
7, 4, 2, 3, 4, 10, 3, 4, 2, 10, 5, 4, 5, 4, 6, 5, 3, 2, 2, 4, 6, 4, 1],
:n0 =>
[28, 21, 32, 35, 35, 38, 30, 43, 49, 53, 31, 35, 46, 53, 61, 40, 29, 44, 52,
55, 61, 31, 48, 44, 42, 53, 56, 71, 43, 43, 43, 40, 44, 70, 75, 71, 37, 31,
42, 46, 47, 55, 63, 91, 43, 39, 35, 32, 53, 49, 75, 64, 69, 64, 49, 29, 40,
27, 48, 43, 61, 77, 55, 60, 46, 28, 33, 32, 46, 57, 56, 78, 58, 52, 31, 28,
46, 42, 45, 63, 71, 69, 43, 50, 31, 34, 54, 46, 58, 62, 52, 41, 34, 52, 63,
59, 88, 62, 47, 53, 57, 74, 68, 61, 45, 45, 62, 73, 53, 39, 45, 51, 55, 41,
53, 51, 42, 46, 54, 32],
:year =>
[-10, -9, -9, -8, -8, -8, -7, -7, -7, -7, -6, -6, -6, -6, -6, -5, -5, -5,
-5, -5, -5, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -4, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -3, -2,
-2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -2, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 4, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 6,
6, 6, 6, 6, 7, 7, 7, 7, 8, 8, 8, 9, 9, 10],
:K => 120
]
oxford[:K] = length(oxford[:r1])
## Model Specification
model = Model(
r0 = Stochastic(1,
@modelexpr(mu, n0, K,
begin
p = invlogit(mu)
Distribution[Binomial(n0[i], p[i]) for i in 1:K]
end
),
false
),
r1 = Stochastic(1,
@modelexpr(mu, alpha, beta1, beta2, year, b, n1, K,
Distribution[
begin
p = invlogit(mu[i] + alpha + beta1 * year[i] +
beta2 * (year[i]^2 - 22.0) + b[i])
Binomial(n1[i], p)
end
for i in 1:K
]
),
false
),
b = Stochastic(1,
@modelexpr(s2,
Normal(0, sqrt(s2))
),
false
),
mu = Stochastic(1,
:(Normal(0, 1000)),
false
),
alpha = Stochastic(
:(Normal(0, 1000))
),
beta1 = Stochastic(
:(Normal(0, 1000))
),
beta2 = Stochastic(
:(Normal(0, 1000))
),
s2 = Stochastic(
:(InverseGamma(0.001, 0.001))
)
)
## Initial Values
inits = [
[:r0 => oxford[:r0], :r1 => oxford[:r1], :alpha => 0, :beta1 => 0,
:beta2 => 0, :s2 => 1, :b => zeros(oxford[:K]), :mu => zeros(oxford[:K])],
[:r0 => oxford[:r0], :r1 => oxford[:r1], :alpha => 1, :beta1 => 1,
:beta2 => 1, :s2 => 10, :b => zeros(oxford[:K]), :mu => zeros(oxford[:K])]
]
## Sampling Scheme
scheme = [AMWG([:alpha, :beta1, :beta2], fill(1.0, 3)),
Slice([:s2], [1.0]),
Slice([:mu], ones(oxford[:K])),
Slice([:b], ones(oxford[:K]))]
setsamplers!(model, scheme)
## MCMC Simulations
sim = mcmc(model, oxford, inits, 12500, burnin=2500, thin=2, chains=2)
describe(sim)
Results¶
Iterations = 2502:12500
Thinning interval = 2
Chains = 1,2
Samples per chain = 5000
Empirical Posterior Estimates:
Mean SD Naive SE MCSE ESS
alpha 0.5657848 0.063005090 0.00063005090 0.0034007318 343.24680
s2 0.0262390 0.030798915 0.00030798915 0.0026076857 139.49555
beta1 -0.0433363 0.016175426 0.00016175426 0.0011077969 213.20196
beta2 0.0054771 0.003567575 0.00003567575 0.0002358424 228.82453
Quantiles:
2.5% 25.0% 50.0% 75.0% 97.5%
alpha 0.44382579 0.5238801 0.5675039 0.60514271 0.6959681
s2 0.00071344 0.0033353 0.0146737 0.03971325 0.1182023
beta1 -0.07451524 -0.0543180 -0.0434426 -0.03212161 -0.0099208
beta2 -0.00104990 0.0028489 0.0056500 0.00774736 0.0136309