No-U-Turn Sampler (NUTS)¶
Implementation of the No-U-Turn Sampler extension (algorithm 6) [48] to Hamiltonian Monte Carlo [65] for simulating autocorrelated draws from a distribution that can be specified up to a constant of proportionality.
Model-Based Constructor¶
-
NUTS(params::ElementOrVector{Symbol}; dtype::Symbol=:forward, args...)¶ Construct a
Samplerobject for NUTS sampling, with the algorithm’s step size parameter adaptively tuned during burn-in iterations. Parameters are assumed to be continuous, but may be constrained or unconstrained.Arguments
params: stochastic node(s) to be updated with the sampler. Constrained parameters are mapped to unconstrained space according to transformations defined by the Stochasticunlist()function.dtype: type of differentiation for gradient calculations. Options are:central: central differencing.:forward: forward differencing.
args...: additional keyword arguments to be passed to theNUTSVariateconstructor.
Value
Returns aSampler{NUTSTune}type object.Example
Stand-Alone Function¶
-
sample!(v::NUTSVariate; adapt::Bool=false)¶ Draw one sample from a target distribution using the NUTS sampler. Parameters are assumed to be continuous and unconstrained.
Arguments
v: current state of parameters to be simulated. When running the sampler in adaptive mode, thevargument in a successive call to the function will contain thetunefield returned by the previous call.adapt: whether to adaptively update theepsilonstep size parameter.
Value
Returnsvupdated with simulated values and associated tuning parameters.Example
The following example samples parameters in a simple linear regression model. Details of the model specification and posterior distribution can be found in the Supplement.
################################################################################ ## Linear Regression ## y ~ N(b0 + b1 * x, s2) ## b0, b1 ~ N(0, 1000) ## s2 ~ invgamma(0.001, 0.001) ################################################################################ using Mamba ## Data data = Dict( :x => [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], :y => [1, 3, 3, 3, 5] ) ## Log-transformed Posterior(b0, b1, log(s2)) + Constant and Gradient Vector logfgrad = function(x::DenseVector) b0 = x[1] b1 = x[2] logs2 = x[3] r = data[:y] .- b0 .- b1 .* data[:x] logf = (-0.5 * length(data[:y]) - 0.001) * logs2 - (0.5 * dot(r, r) + 0.001) / exp(logs2) - 0.5 * b0^2 / 1000 - 0.5 * b1^2 / 1000 grad = [ sum(r) / exp(logs2) - b0 / 1000, sum(data[:x] .* r) / exp(logs2) - b1 / 1000, -0.5 * length(data[:y]) - 0.001 + (0.5 * dot(r, r) + 0.001) / exp(logs2) ] logf, grad end ## MCMC Simulation with No-U-Turn Sampling n = 5000 burnin = 1000 sim = Chains(n, 3, start = (burnin + 1), names = ["b0", "b1", "s2"]) theta = NUTSVariate([0.0, 0.0, 0.0], logfgrad) for i in 1:n sample!(theta, adapt = (i <= burnin)) if i > burnin sim[i, :, 1] = [theta[1:2]; exp(theta[3])] end end describe(sim)
NUTSVariate Type¶
Declaration¶
const NUTSVariate = SamplerVariate{NUTSTune}
Fields¶
value::Vector{Float64}: simulated values.tune::NUTSTune: tuning parameters for the sampling algorithm.
Constructors¶
-
NUTSVariate(x::AbstractVector{T<:Real}, epsilon::Real, logfgrad::Function; target::Real=0.6)¶ -
NUTSVariate(x::AbstractVector{T<:Real}, logfgrad::Function; target::Real=0.6) Construct a
NUTSVariateobject that stores simulated values and tuning parameters for NUTS sampling.Arguments
x: initial values.epsilon: step size parameter.logfgrad: function that takes a singleDenseVectorargument of parameter values at which to compute the log-transformed density (up to a normalizing constant) and gradient vector, and returns the respective results as a tuple. Ifepsilonis not specified, the function is used by the constructor to generate an initial step size value.target: target acceptance rate for the algorithm.
Value
Returns aNUTSVariatetype object with fields set to the suppliedxand tuning parameter values.
NUTSTune Type¶
Declaration¶
type NUTSTune <: SamplerTune
Fields¶
logfgrad::Nullable{Function}: function supplied to the constructor to compute the log-transformed density and gradient vector, or null if not supplied.adapt::Bool: whether the proposal distribution is being adaptively tuned.alpha::Float64: cumulative acceptance probabilities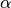 from leapfrog steps.
from leapfrog steps.epsilon::Float64: updated value of the step size parameter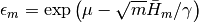 if
if m > 0, and the user-supplied value otherwise.epsbar::Float64: dual averaging parameter, defined as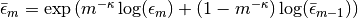 .
.gamma::Float64: dual averaging parameter, fixed at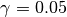 .
.Hbar::Float64: dual averaging parameter, defied as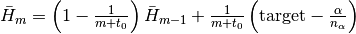 .
.kappa::Float64: dual averaging parameter, fixed at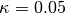 .
.m::Int: number of adaptive update iterations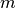 that have been performed.
that have been performed.mu::Float64: dual averaging parameter, defined as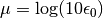 .
.nalpha::Int: the total number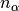 of leapfrog steps performed.
of leapfrog steps performed.t0::Float64: dual averaging parameter, fixed at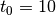 .
.target::Float64: target acceptance rate for the adaptive algorithm.